Fatigue crack growth in the welding nuggetof FSW joints of a 6060 aluminum alloy
6060铝合金搅拌摩擦焊焊接接头的疲劳裂纹扩展行为
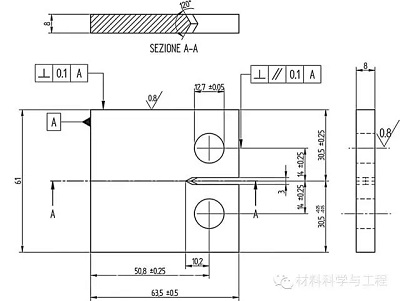
Friction stir welded butt joints were performed on 8 mm thick sheets made of AA6060 T6 aluminum alloy by means of a CNC machine tool, at feed rates between 117 and 683 mm/min and tool rotational speed between 838 and 1262 rpm.
利用数控机床进行搅拌摩擦焊将8mm厚的AA6060 T6铝合金对接,进给速度为117~683mm/min,工具转速为 838~1262 rpm。
Tensile tests, metallographic analyses and micro-Vickers tests were carried out to evaluate the mechanical properties of the joints as a function of the process parameters.
通过拉伸实验、金相分析和显微硬度测试,研究了焊接接头力学性能与工艺参数之间的关系。
The fatigue behavior was studied by means of crack growth tests performed according to ASTM E647 standard on CT specimens, with propagation in the middle of joint along the weld nugget.
依据ASTM E647标准,采用CT试样研究了疲劳裂纹在焊核区中心的扩展行为。
The results show the influence of welding process parameters on mechanical properties and fatigue behavior.
实验结果给出了焊接工艺参数对该铝合金力学性能和疲劳行为的影响。
Reduction of UTS of about 20–30% with respect to base material occurred with rupture in the softened zone of welding, usually HAZ.
与母材相比,焊接后的试样抗拉强度减小了大约20~30%,试样在软化区发生断裂,该区域通常是热影响区。
In this range, slight variations of joint efficiency were observed with f/S ratio, while the width of the softening area increases for decreasing values of this parameter.
不同f/S比(进给速度/工具转速)下的接头系数略有波动,软化区的宽度随着f/S比的减小而增大。
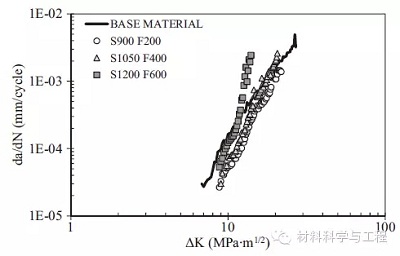
Fatigue crack growth was always slower thanthat in the base material at low △K below 12 MPa m1/2. The effect of non-optimal welding parameterswas evident at intermediate and high △K, due to defects,such as tunnels, that cause dramatic increase of propagation rate up to fivetimes higher than the base material.
当△K小于12 MPa m1/2时,焊接试样的疲劳裂纹扩展速率总是小于母材的。△K处于中等和较高水平时,焊接试样的疲劳裂纹扩展速率是母材的5倍。这是由于非优化的焊接工艺产生了各种缺陷(比如隧道状的缺陷)。
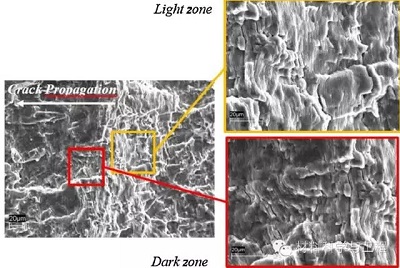
疲劳断口形貌
想深入阅读的读者,请查看论文:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924013614000272
*本文系原创整理文章
点击标题,查看相关阅读:
欢迎投稿:mse_material@163.com
欢迎合作:service@cailiaokexue.com